|
C.1
Labels
C.1
The label for each hazardous chemical shall include
the product identifier used on the safety data sheet.
C.1.1 The labels on shipped containers shall
also include the name, address, and telephone number
of the chemical manufacturer, importer, or responsible
party.
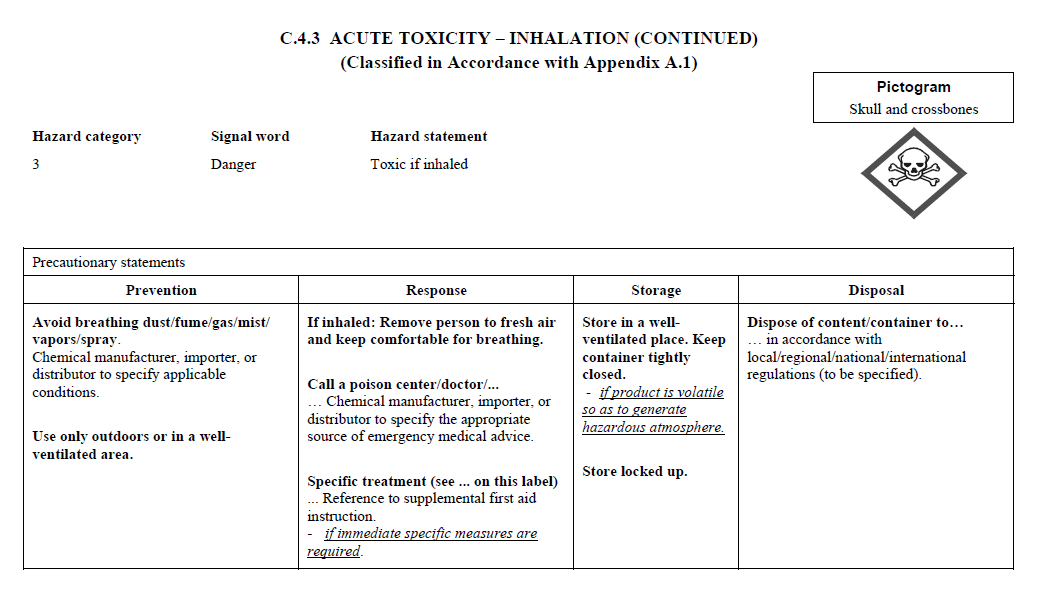
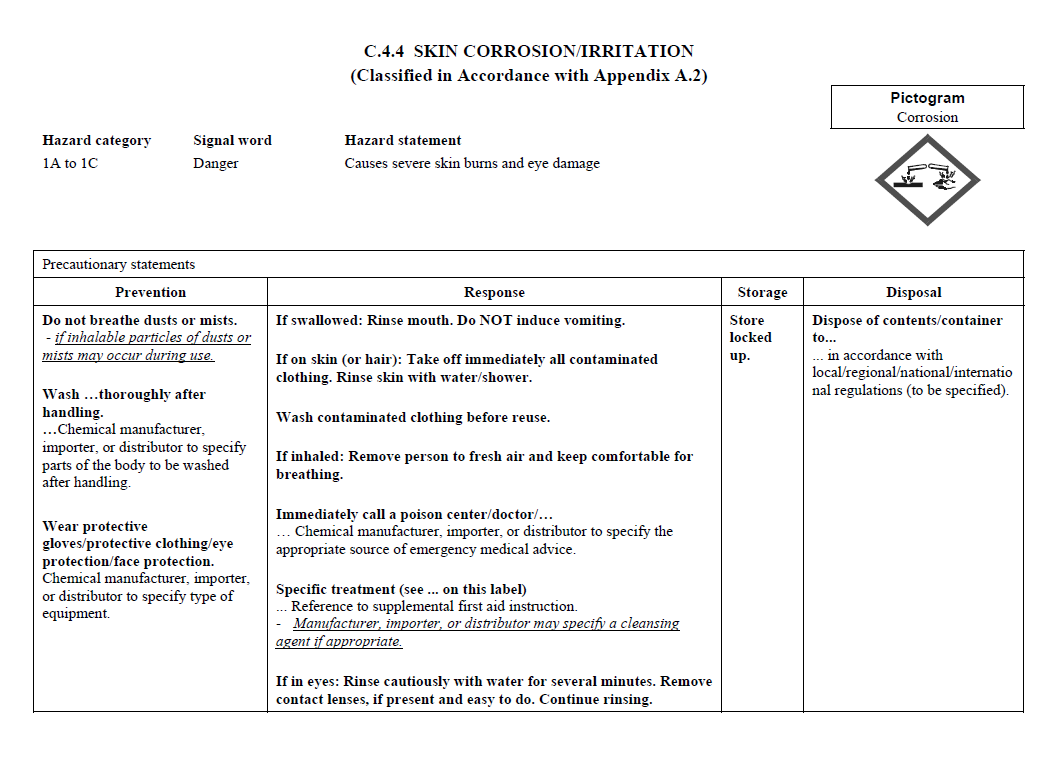
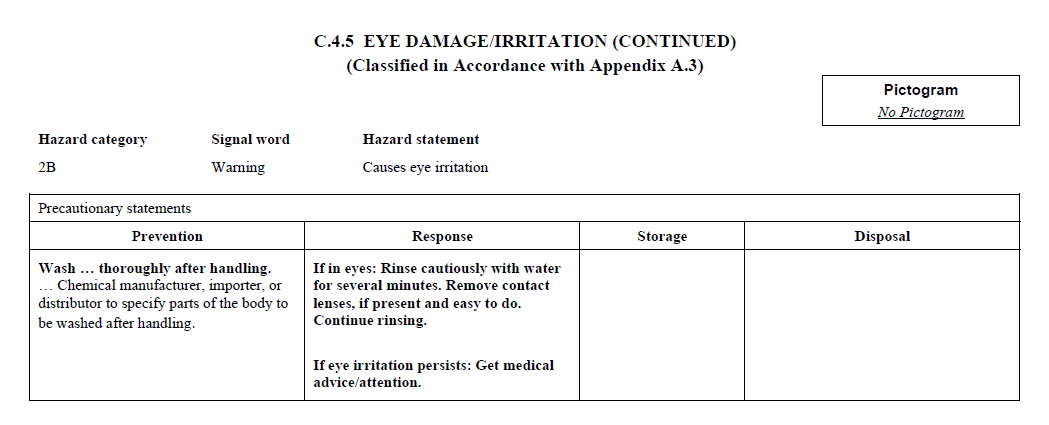
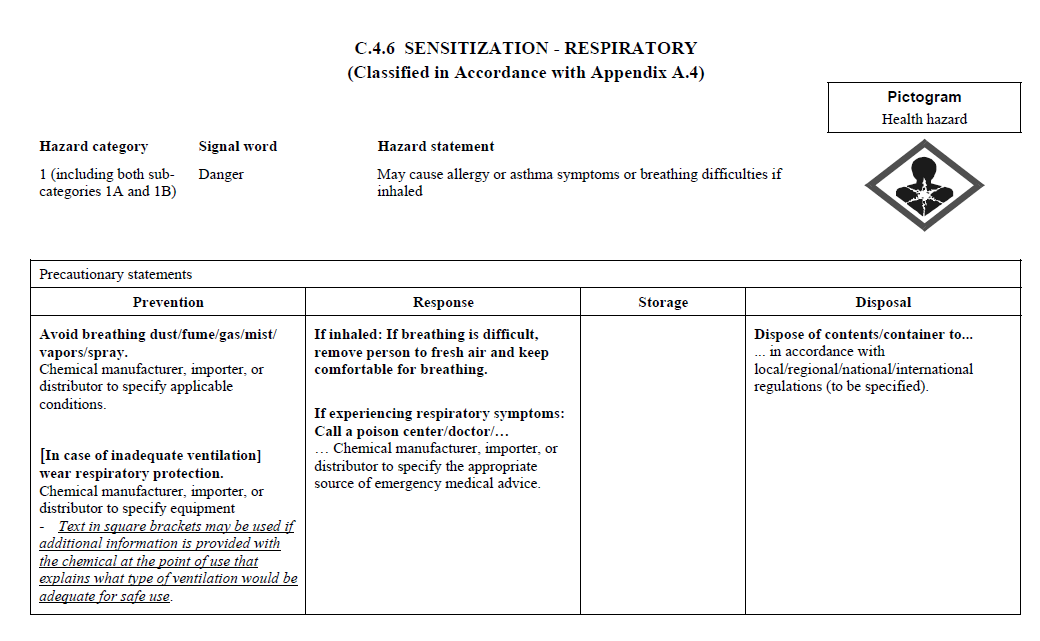
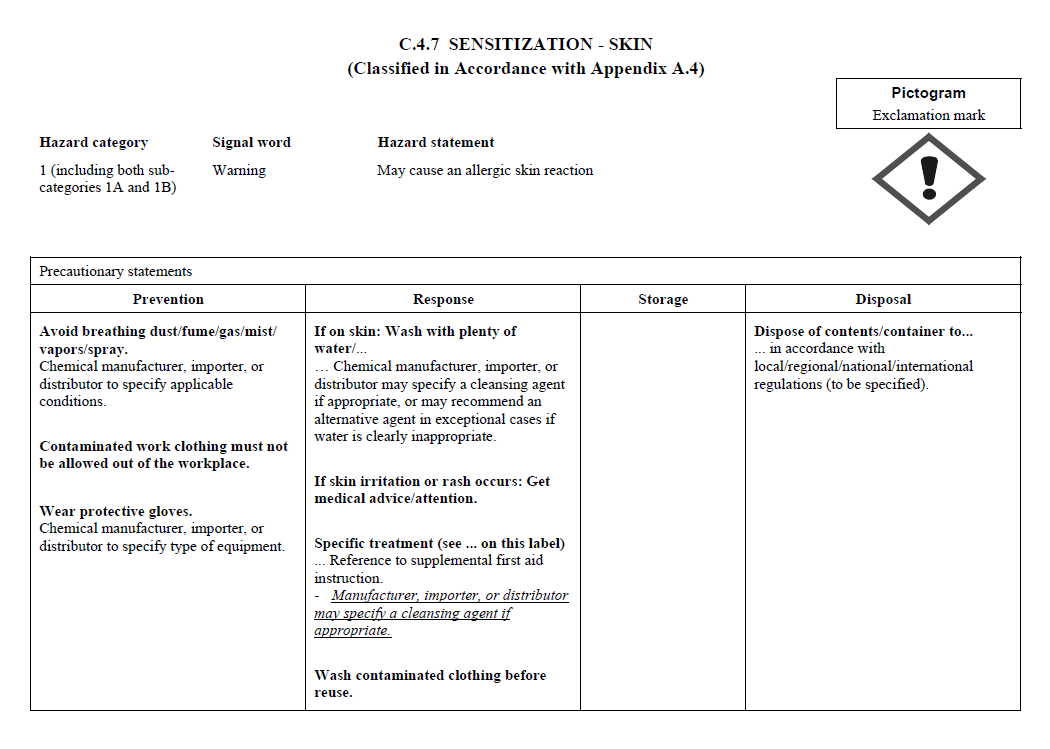
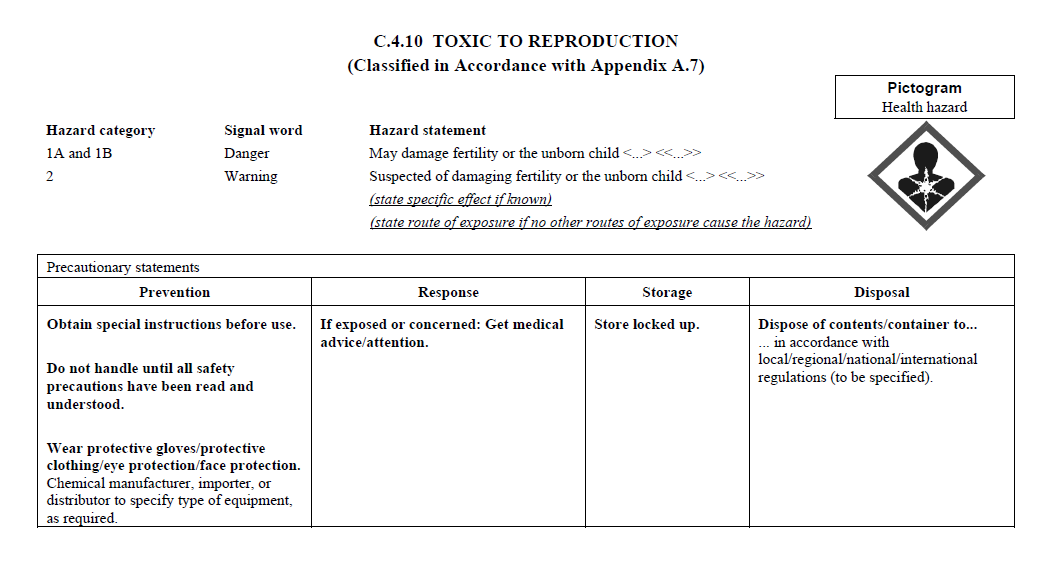
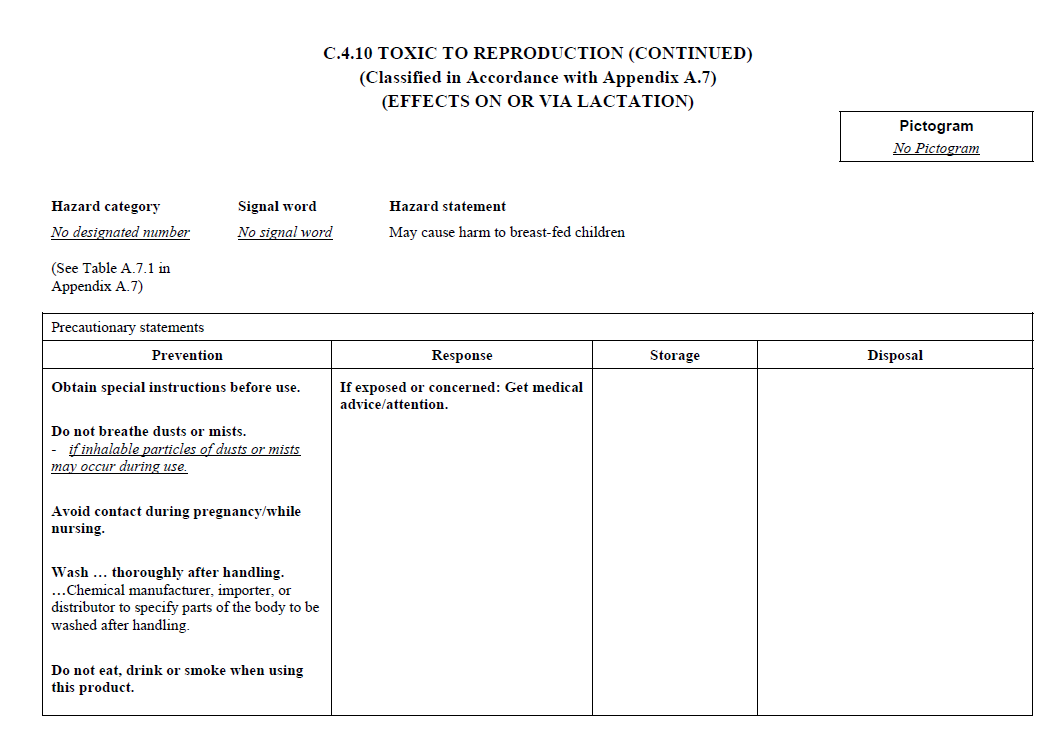
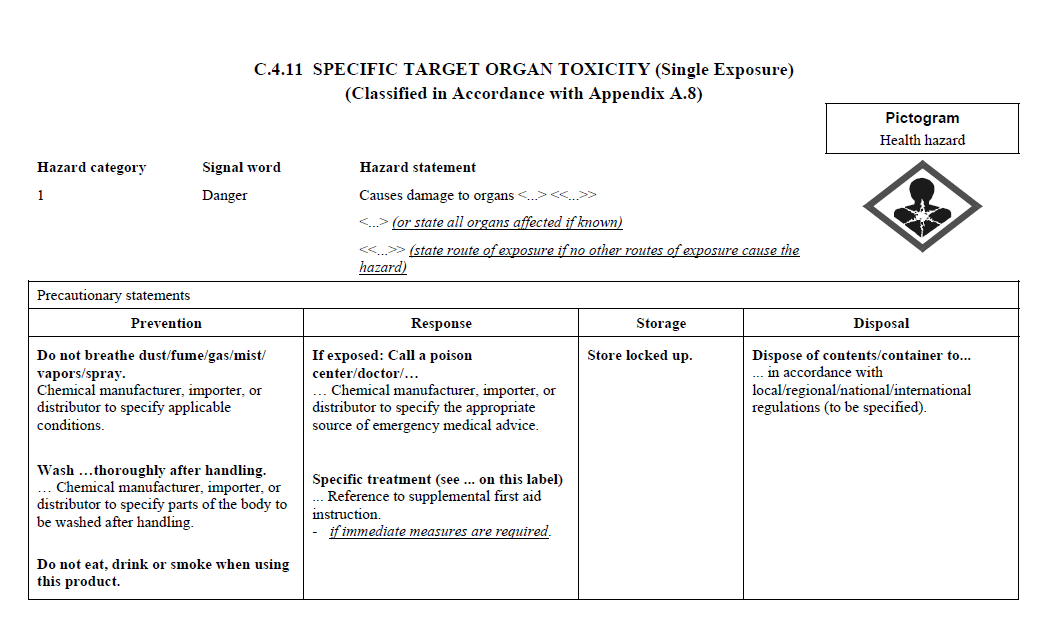
C.2 The label for each hazardous chemical that
is classified shall include the signal word, hazard
statement(s), pictogram(s), and precautionary statement(s)
specified in C.4 for each hazard class and associated
hazard category, except as provided for in C.2.1 through
C.2.4.
C.2.1
Precedence of hazard information
C.2.1.1
If the signal word “Danger” is included,
the signal word “Warning” shall not appear;
C.2.1.2 If the skull and crossbones pictogram
is included, the exclamation mark pictogram shall
not appear where it is used for acute toxicity;
C.2.1.3 If the corrosive pictogram is included,
the exclamation mark pictogram shall not appear where
it is used for skin or eye irritation;
C.2.1.4 If the health hazard pictogram is included
for respiratory sensitization, the exclamation mark
pictogram shall not appear where it is used for skin
sensitization or for skin or eye irritation.
C.2.2
Hazard statement text
C.2.2.1
The text of all applicable hazard statements shall
appear on the label, except as otherwise specified.
The information in italics shall be included as part
of the hazard statement as provided. For example:
“causes damage to organs (state all organs affected)
through prolonged or repeated exposure (state route
of exposure if no other routes of exposure cause the
hazard)”. Hazard statements may be combined where
appropriate to reduce the information on the label
and improve readability, as long as all of the hazards
are conveyed as required.
C.2.2.2 If the chemical manufacturer, importer,
or responsible party can demonstrate that all or part
of the hazard statement is inappropriate to a specific
substance or mixture, the corresponding statement
may be omitted from the label.
C.2.3
Pictograms
C.2.3.1
Pictograms shall be in the shape of a square set at
a point and shall include a black hazard symbol on
a white background with a red frame sufficiently wide
to be clearly visible. A square red frame set at a
point without a hazard symbol is not a pictogram and
is not permitted
on the label.
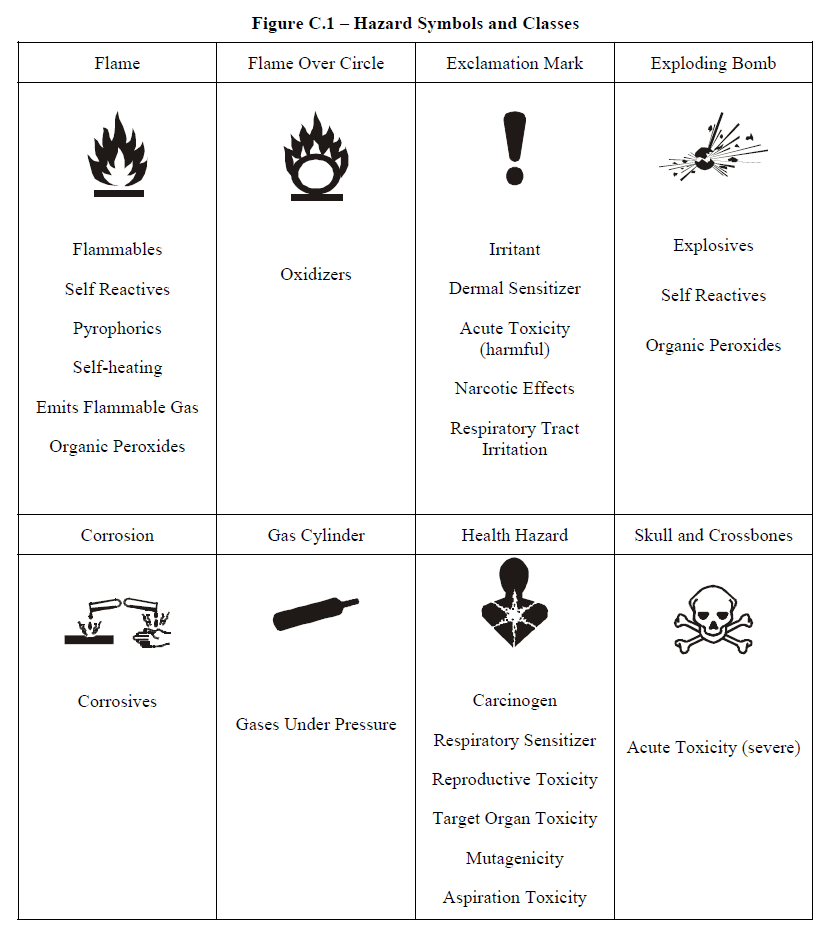
C.2.3.2
One of eight standard hazard symbols shall be used
in each pictogram. The eight hazard symbols are depicted
in Figure C.1. A pictogram using the exclamation mark
symbol is presented in Figure C.2, for the purpose
of illustration.

C.2.3.3
Where a pictogram required by the Department of
Transportation under Title 49 of the Code of Federal
Regulations appears on a shipped container, the pictogram
specified in C.4 for the same hazard shall not appear.
C.2.4
Precautionary statement text
C.2.4.1
There are four types of precautionary statements presented,
“prevention,” “response,” “storage,”
and “disposal.” The core part of the precautionary
statement is presented in bold print. This
is the text, except as otherwise specified, that shall
appear on the label. Where additional information
is required, it is indicated in plain text.
C.2.4.2 When a backslash or diagonal mark (
/ ) appears in the precautionary statement text, it
indicates that a choice has to be made between the
separated phrases. In such cases, the chemical manufacturer,
importer, or responsible party can choose the most
appropriate phrase(s). For example, “Wear protective
gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection”
could read “wear eye protection”.
C.2.4.3 When three full stops (…) appear
in the precautionary statement text, they indicate
that all applicable conditions are not listed. For
example, in “Use explosion-proof electrical/ventilating/lighting/.../equipment”,
the use of “...” indicates that other equipment
may need to be specified. In such cases, the chemical
manufacturer, importer, or responsible party can choose
the other conditions to be specified.
C.2.4.4
When text in italics is used in a precautionary statement,
this indicates specific conditions applying to the
use or allocation of the precautionary statement.
For example, “Use explosion-proof electrical/ventilating/lighting/.../equipment”
is only required for flammable solids “if
dust clouds can occur”. Text in italics is
intended to be an explanatory, conditional note and
is not intended to appear on the label.
C.2.4.5 Where square brackets ( [ ] ) appear
around text in a precautionary statement, this indicates
that the text in square brackets is not appropriate
in every case and should be used only in certain circumstances.
In these cases, conditions for use explaining when
the text should be used are provided. For example,
one precautionary statement states: "[In case
of inadequate ventilation] wear respiratory protection."
This statement is given with the condition for use
"-. text in square brackets may be used if additional
information is provided with the chemical at the point
of use that explains what type of ventilation would
be adequate for safe use". This means that, if
additional information is provided with the chemical
explaining what type of ventilation would be adequate
for safe use, the text in square brackets should be
used and the statement would read: -"In case
of inadequate ventilation wear respiratory protection.-"
However, if the chemical is supplied without such
ventilation information, the text in square brackets
should not be used, and the precautionary statement
should read: -"Wear respiratory protection."
C.2.4.6 Precautionary statements may be combined
or consolidated to save label space and improve readability.
For example, "Keep away from heat, sparks and
open flame," "Store in a well-ventilated
place", and "Keep cool", can be combined
to read "keep away from heat, sparks and open
flame and store in a cool, well-ventilated place."
C.2.4.7 In most cases, the precautionary statements
are independent (e.g., the phrases for explosive hazards
do not modify those related to certain health hazards,
and products that are classified for both hazard classes
shall bear appropriate precautionary statements for
both). Where a chemical is classified for a number
of hazards, and the precautionary statements are similar,
the most stringent shall be included on the label
(this will be applicable mainly to preventive measures).
An order of precedence may be imposed by the chemical
manufacturer, importer or responsible party in situations
where phrases concern "Response." Rapid
action may be crucial. For example, if a chemical
is carcinogenic and acutely toxic, rapid action may
be crucial, and first aid measures for acute toxicity
will take precedence over those for long-term effects.
In addition, medical attention to delayed health effects
may be required in cases of incidental exposure, even
if not associated with immediate symptoms of intoxication.
C.2.4.8 If the chemical manufacturer, importer,
or responsible party can demonstrate that a precautionary
statement is inappropriate to a specific substance
or mixture, the precautionary statement may be omitted
from the label.
C.3
Supplementary hazard information
C.3.1
To ensure that non-standardized information does not
lead to unnecessarily wide variation or undermine
the required information, supplementary information
on the label is limited to when it provides further
detail and does not contradict or cast doubt on the
validity of the standardized hazard information.
C.3.2 Where the chemical manufacturer, importer,
or distributor chooses to add supplementary information
on the label, the placement of supplemental information
shall not impede identification of information required
by this section.
C.3.3 Where an ingredient with unknown acute
toxicity is used in a mixture at a concentration >=
1%, and the mixture is not classified based on testing
of the mixture as a whole, a statement that X% of
the mixture consists of ingredient(s) of unknown acute
toxicity is required on the label.
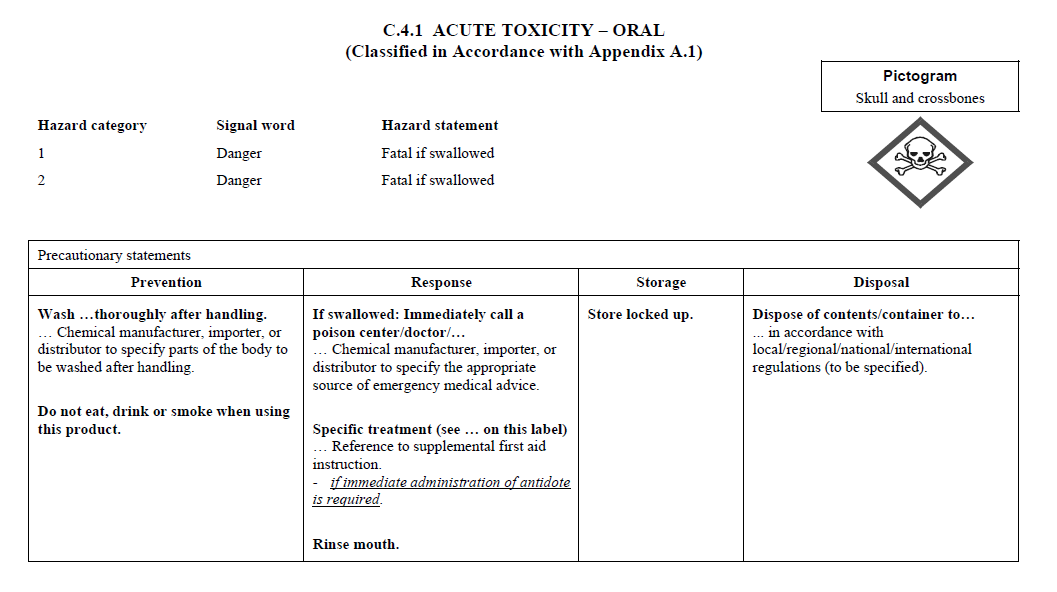
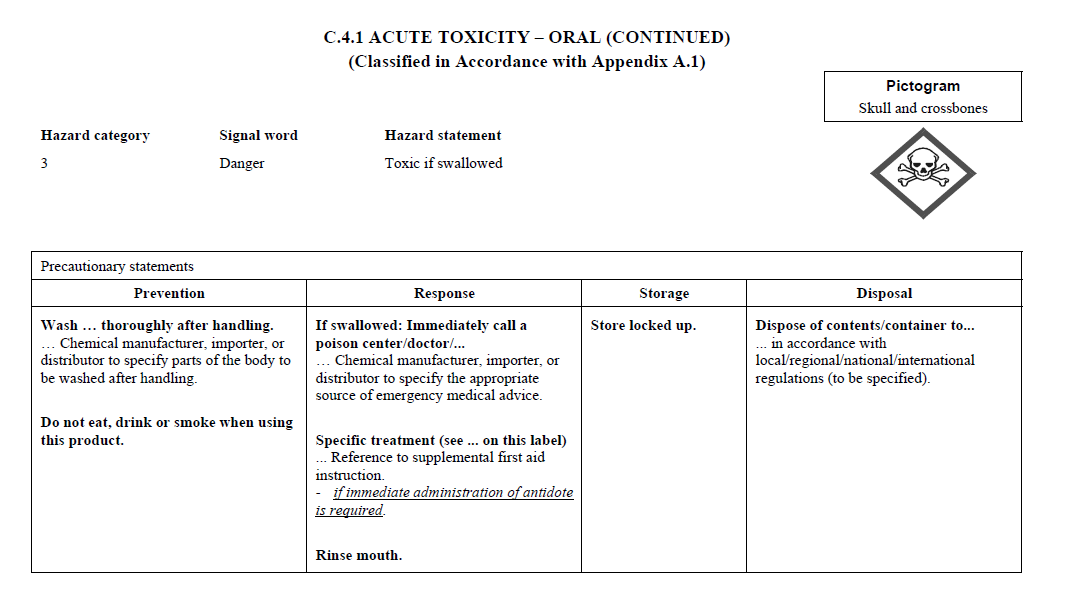
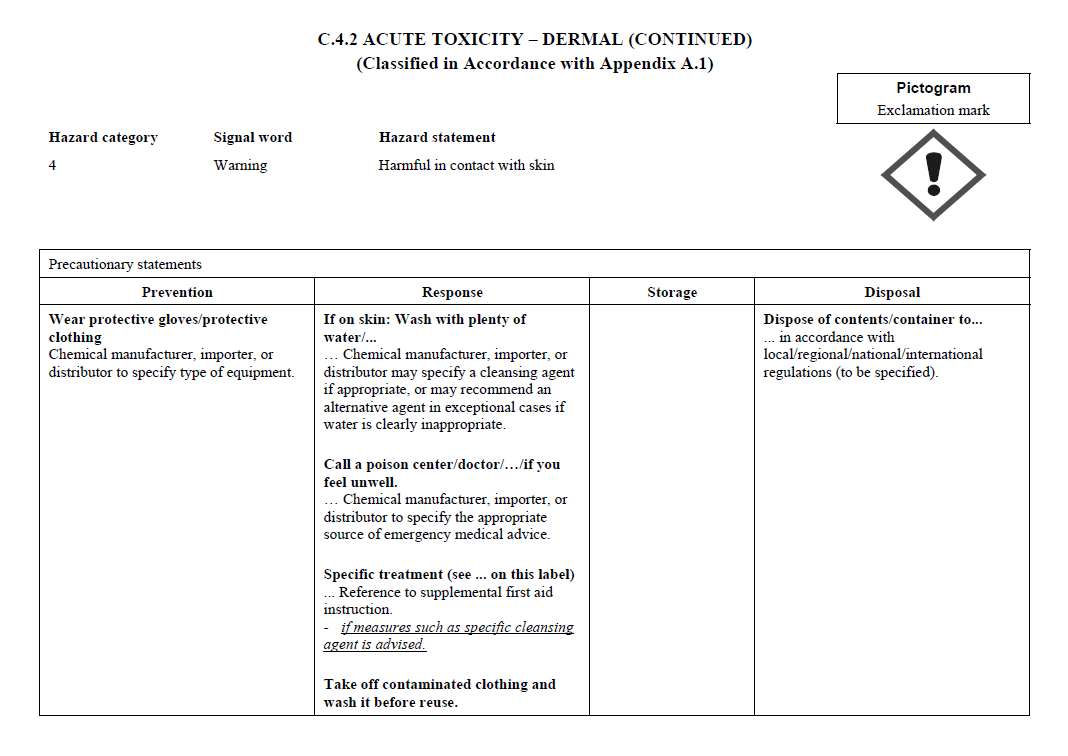
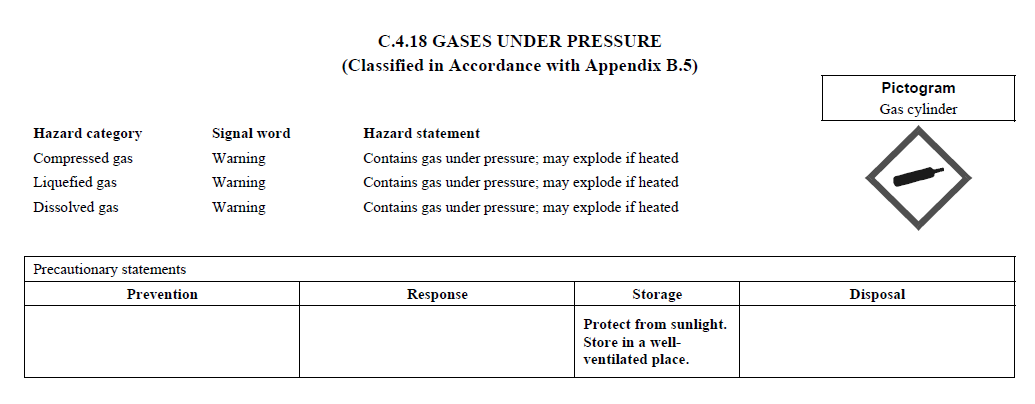
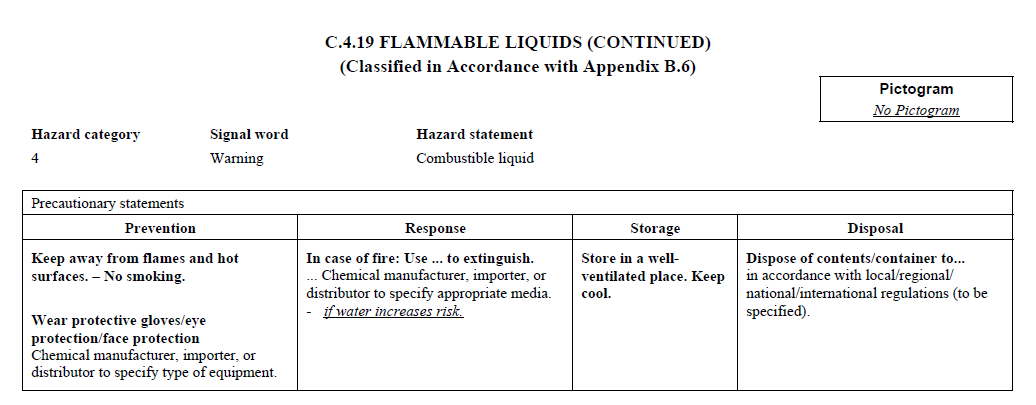
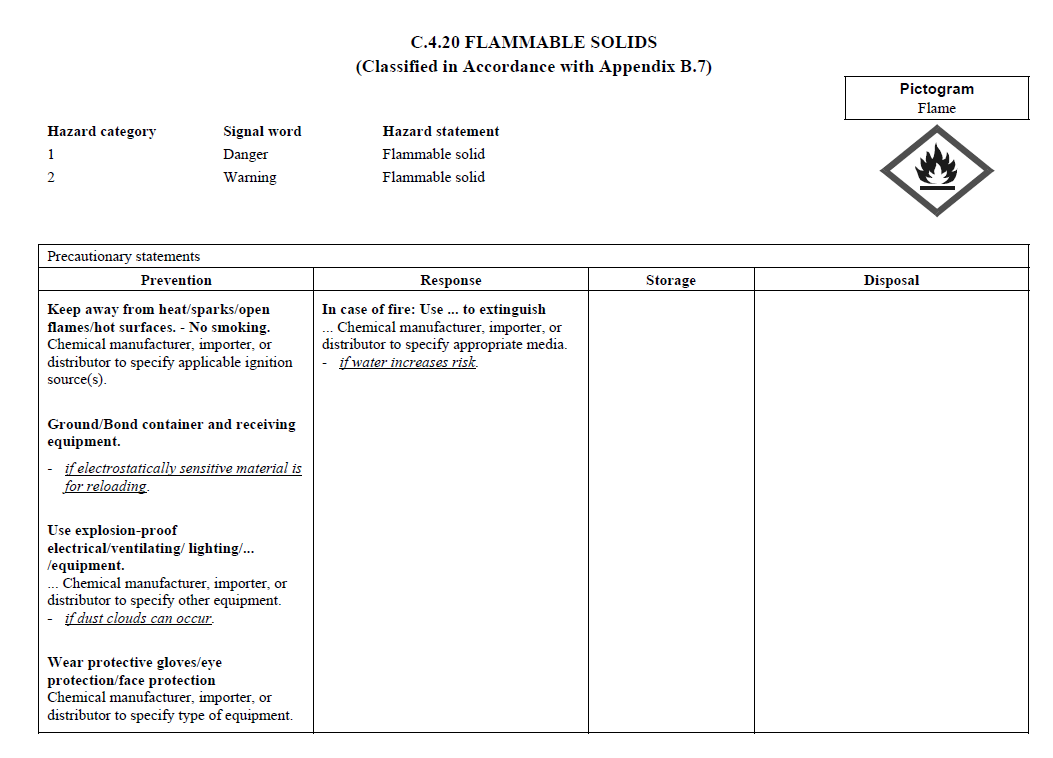
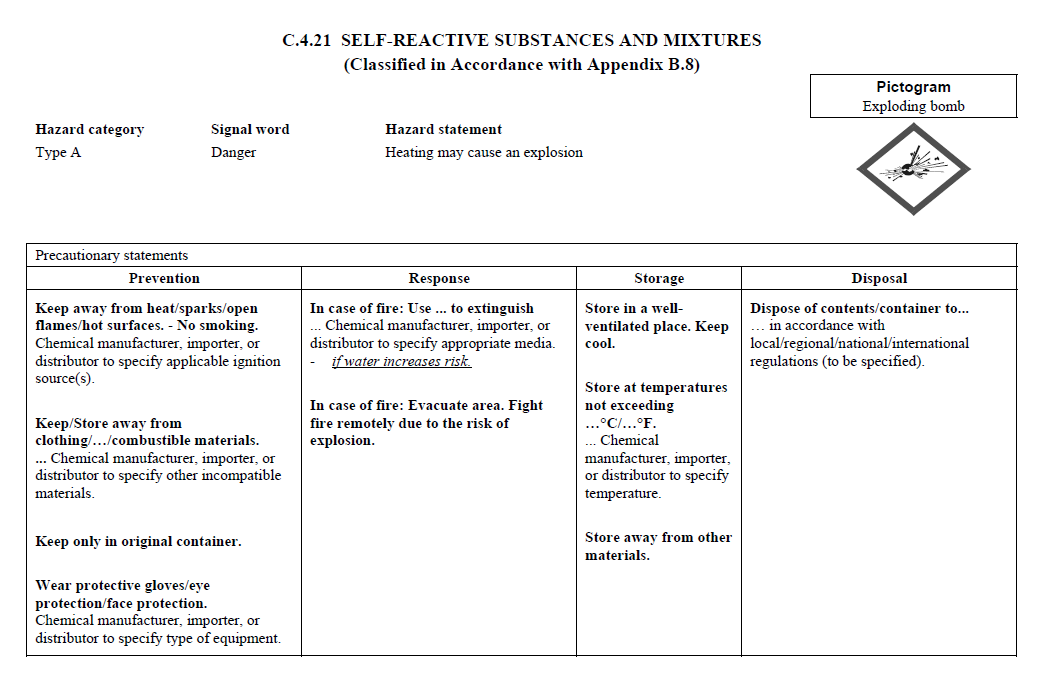
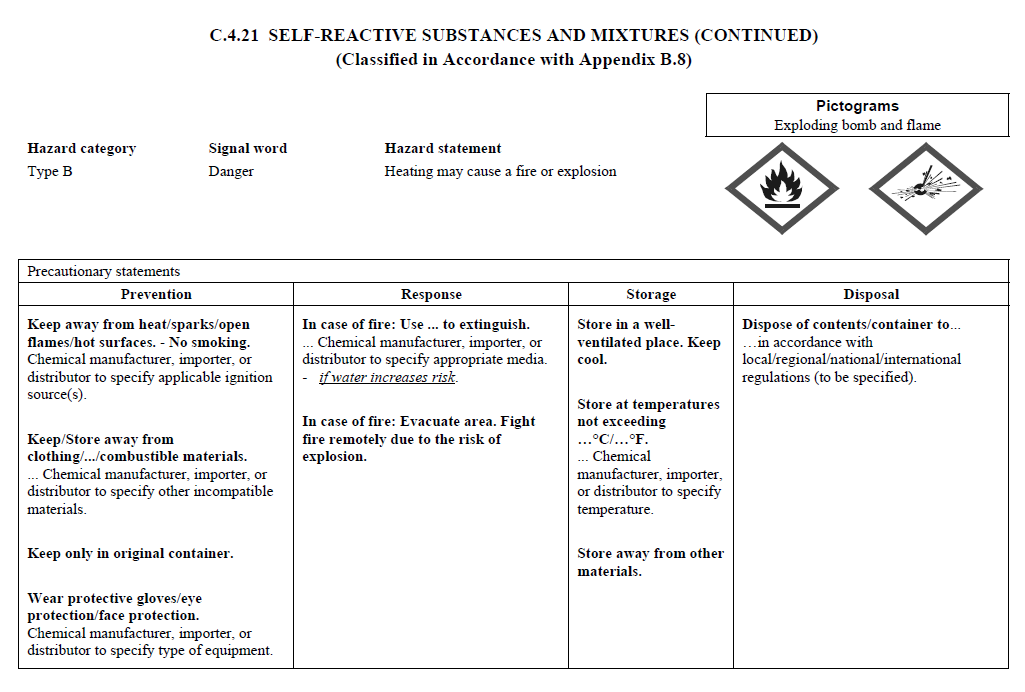
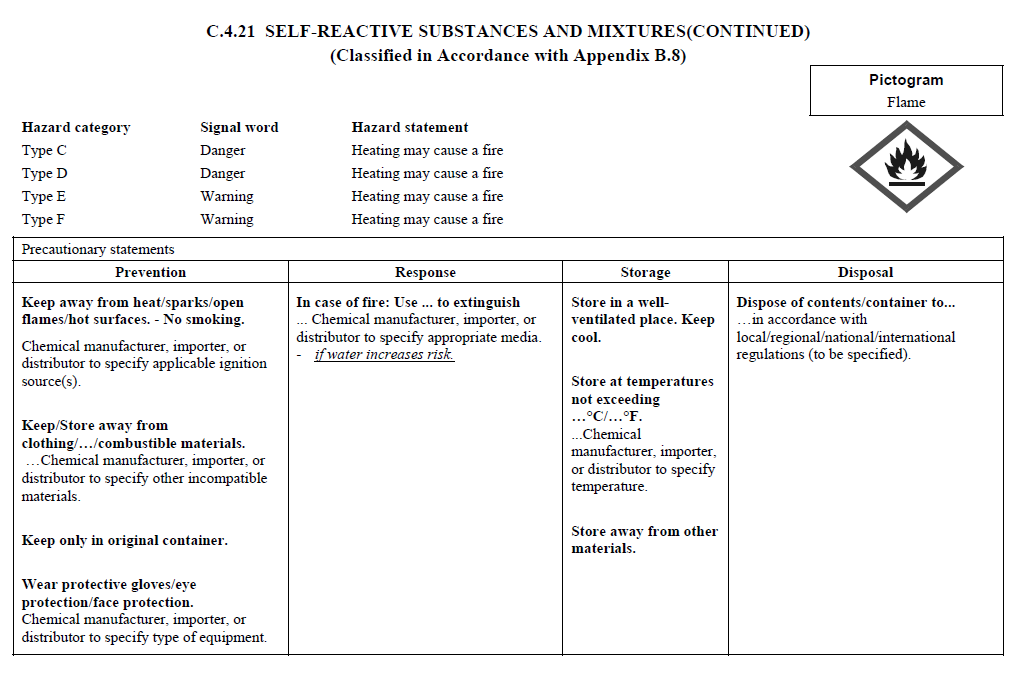
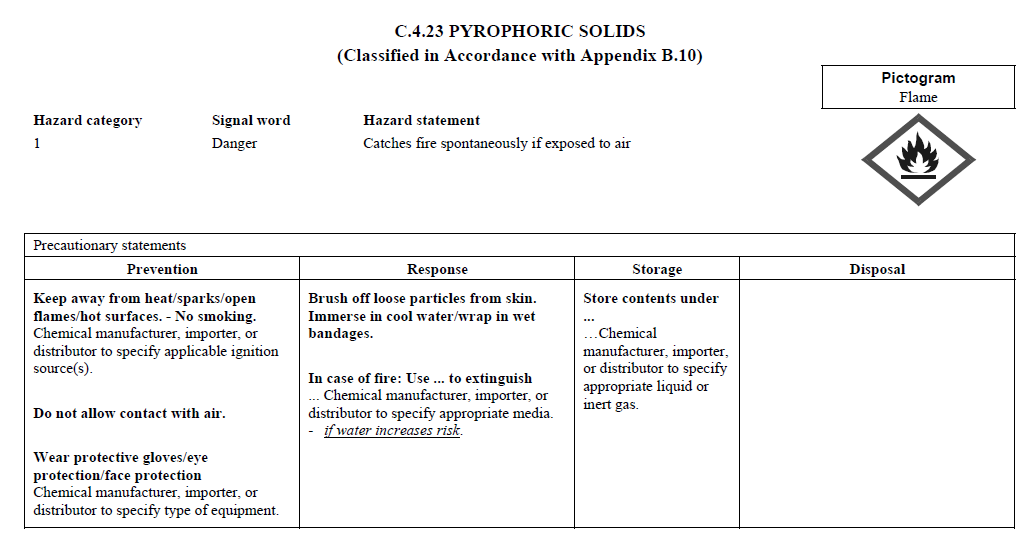
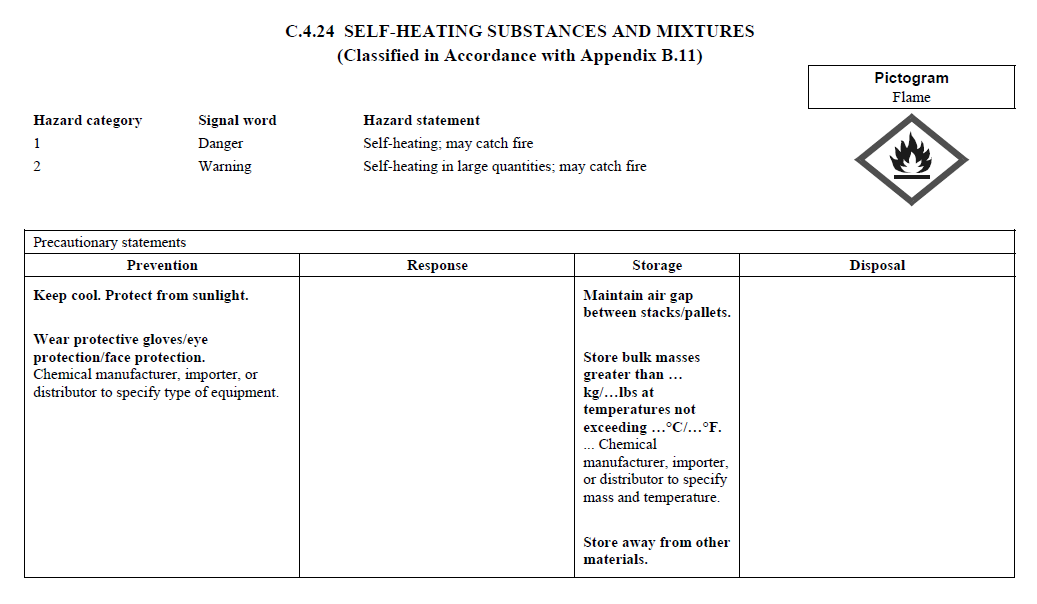
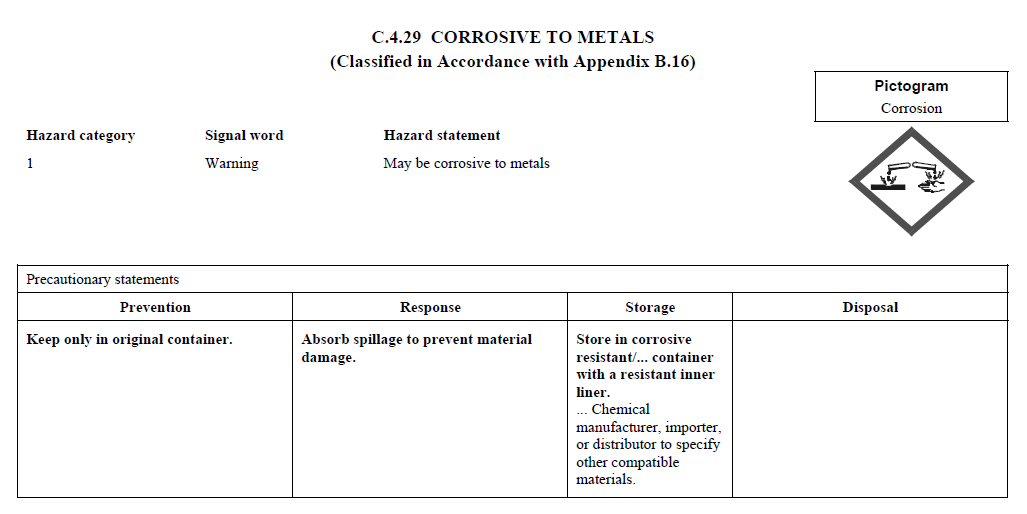
C.4
REQUIREMENTS FOR SIGNAL WORDS, HAZARD STATEMENTS, PICTOGRAMS,
AND PRECAUTIONARY STATEMENTS





















|

